Vapor management: Difference between revisions
Moved LM text to LM header and replaced wiht VM text |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Vapour Management (VM) | Vapour Management (VM) | ||
The vapour management column is a relatively new design. While Liquid Management condenses everything and manages the reflux ratio by splitting the liquid, the VM splits the vapour into two streams, and then condenses each separately: | The vapour management column is a relatively new design. While Liquid Management condenses everything and manages the reflux ratio by splitting the liquid, the VM splits the vapour into two streams, and then condenses each separately: | ||
[[File:Vapor_Management.png|thumb|120px|right|Vapor Management Head]] | [[File:Vapor_Management.png|thumb|120px|right|Vapor Management Head]] | ||
Revision as of 05:07, 19 September 2017
Vapour Management (VM)
The vapour management column is a relatively new design. While Liquid Management condenses everything and manages the reflux ratio by splitting the liquid, the VM splits the vapour into two streams, and then condenses each separately:
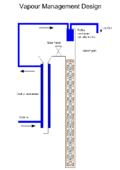
VM
Because a VM splits the stream of vapour before reflux is generated, with the valve set the valve wide open (assuming a full size takeoff port), you're getting roughly 1:1 reflux ratio regardless of the amount of vapour. While with an LM, adjustment would be needed as the production rate decreases, in a VM the reflux ratio will stay constant and output will fall; lets say the valve is still wide open, at the beginning 100mls/min = 50:50 = 1:1, and later 75mls/min = 37.5:37.5 = 1:1. The valve on a VM sets the reflux ratio, not the takeoff amount, and as the reflux ratio is what you want to set and keep constant over hearts. Many people see this a one of the key benefits of a VM still.
Also, because of this, the valve settings for VM will remain constant over different charges or the still (which will probably produce at different rates) changes in heat input, and so on and so forth. Anything that varies the rate of production of vapour requires a change in valve settings on an LM. A VM you just leave. Well, for hearts anyway. Any column you choose will require some amount of adjustment for foreshots, heads and tails, but again, the nice thing about the VM is PREDICTABILITY. you can remember what ratio you like to take off heads at, set it, do other things around the shed and change it when you've taken off enough. Instead of having to keep adjusting a valve when tails is looming, you just wait until the thermometer budges, knock back the valve a bit til it goes down, when it budges again open her up and take off the measly litre of tails. Or don't even bother. Tails from a reflux are so gross you won't want them anywhere near your product. The VM is generally acknowledged as the easiest design to run.
A VM has drawbacks too. The first is that it's quite hard to discover the reflux ratio (here is my experiment to calculate mine). This isn't a major problem, as you don't really need to know. The other drawback is you are limited in how little reflux you can produce (ie the minimum reflux ratio, because the VM cannot (without simple modification) get less than about 1:1 reflux ratio (unless you have a small takeoff port, in which case the minimum ratio will be more like 4:1), it is (imho) unsuited for flavoured spirits. I personally consider the VM a one trick pony, neutral and only neutral. But then again, if you want flavour, get a pot still.
The other main drawback of a VM is it is less effective for heads extraction when compared to a good LM design. This results in a slightly higher proportion of your total run being heads. To get the advantage of both LM and VM in a single build, many combine them, and have a VM takeoff (for hearts) below a set of slant plates for LM takeoff (for heads extraction). Another option for adding LM functionality to a VM stills is to use a horizontal condenser, like the Crossflow Condenser or Thors Hammer (search for them for more info).
Original Post by Kiwistiller, edited by Bushman, Can be found here.