Butanol: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Uncle Jesse (talk | contribs) Adding images |
Uncle Jesse (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
These butanol isomers, due to their different structures, have somewhat different melting and boiling points. All are moderately miscible in [[Water|water]] and used as a base for perfumes. For the purposes of [[Distillation|distillation]], butanol is considered to be a [[Fusel_oils|fusel oil]]. Like most alcohols, they are poisonous. | These butanol isomers, due to their different structures, have somewhat different melting and boiling points. All are moderately miscible in [[Water|water]] and used as a base for perfumes. For the purposes of [[Distillation|distillation]], butanol is considered to be a [[Fusel_oils|fusel oil]]. Like most alcohols, they are poisonous. | ||
Latest revision as of 01:23, 15 December 2022
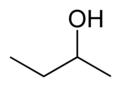
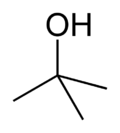
Butanol is a higher alcohol with a 4 carbon atoms and a general formula of C4H10O. There are 4 different isomeric structures for butanol:
|

|
| |
| n-butanol | sec-butanol | isobutanol | tert-butanol |
These butanol isomers, due to their different structures, have somewhat different melting and boiling points. All are moderately miscible in water and used as a base for perfumes. For the purposes of distillation, butanol is considered to be a fusel oil. Like most alcohols, they are poisonous.