Diacetyl: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Uncle Jesse (talk | contribs) Adding image |
Uncle Jesse (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[file:diacetyl.gif|thumb|232px|right|Diacetyl]] | [[file:diacetyl.gif|thumb|232px|right|Diacetyl]] | ||
Diacetyl arises naturally as a byproduct of [[fermentation]]. At low levels, diacetyl contributes a slipperiness to the feel of the alcoholic beverage in the mouth. As levels increase, it imparts a buttery or butterscotch flavor. It is generally considered a fault at too high of a level in [[beer]] or [[ | Diacetyl arises naturally as a byproduct of [[fermentation]]. At low levels, diacetyl contributes a slipperiness to the feel of the alcoholic beverage in the mouth. As levels increase, it imparts a buttery or butterscotch flavor. It is generally considered a fault at too high of a level in [[beer]] or [[distillate]]s. The simplest way to reduce diacetyl is to increase fermentation temperatures near the end - called a Diacetyl Rest. The remaining yeast remove it by storing it in the yeast cell where it cannot be tasted. | ||
==External Links== | ==External Links== | ||
* [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Diacetyl Diacetyl at Wikipedia] | *[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Diacetyl Diacetyl at Wikipedia] | ||
*[https://byo.com/bock/item/303-brewing-science-controlling-diacetyl Controlling Diacetyl at BYO.com] | |||
[[Category:Yeast]] | [[Category:Yeast]] | ||
[[Category:Fermentation]] | [[Category:Fermentation]] | ||
[[Category:Glossary]] | [[Category:Glossary]] | ||
Latest revision as of 01:06, 8 October 2017
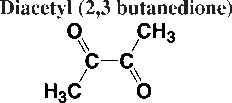
Diacetyl arises naturally as a byproduct of fermentation. At low levels, diacetyl contributes a slipperiness to the feel of the alcoholic beverage in the mouth. As levels increase, it imparts a buttery or butterscotch flavor. It is generally considered a fault at too high of a level in beer or distillates. The simplest way to reduce diacetyl is to increase fermentation temperatures near the end - called a Diacetyl Rest. The remaining yeast remove it by storing it in the yeast cell where it cannot be tasted.