HETP: Difference between revisions
m →External Links: formatting |
m Added HETP chart image |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[file:HETP.jpg|thumb|185px|right|HETP purity Chart]] | |||
'''H'''eight '''E'''quivalent of '''T'''heoretical '''P'''late | '''H'''eight '''E'''quivalent of '''T'''heoretical '''P'''late | ||
Revision as of 06:22, 8 January 2018
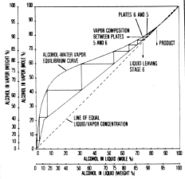
Height Equivalent of Theoretical Plate
For distilling the higher the HETP the more pure the product will be. It is a useful calculation for trying to achieve azeotrope for vodka and other neutrals.
A theoretical plate in many separation processes is a hypothetical zone or stage in which two phases, such as the liquid and vapor phases of a substance, establish an equilibrium with each other. Such equilibrium stages may also be referred to as an equilibrium stage, ideal stage, or a theoretical tray. The performance of many separation processes depends on having a series of equilibrium stages and is enhanced by providing more such stages. In other words, having more theoretical plates increases the efficiency of the separation process be it either a distillation, absorption, chromatographic, adsorption or similar process.